Silicosis is an uncommon disease but is common among special occupations. Inhalation of silica causes the disease as it is a substance that can cause fibrosis of the lungs. This substance increases swelling and inflammation of the lung initially which later leads to the formation of scar tissue called fibrosis. Silica is a substance found in stones and rocks which can be inhaled when it is produced as fine dust within some industries.
Occupations at Risk for Silicosis
- Stone masonry and stone cutting – especially with sandstone
- Sandblasters
- Pottery and ceramic manufacturing industry
- Construction and demolition – as a result of exposure to concrete and paving material
- Mining and quarrying

Clinical Manifestations
These patients normally don’t get any symptoms and signs initially. The disease takes a few years to become symptomatic. A person working in a high-risk occupation must get exposed to silica dust for at least 10- 20 years to get the disease although it can occur in a shorter period as well.
The main symptoms are,

- Persistent cough
- Increased feeling of fatigue
- Wheezing
- Chest pain
- Loss of weight
- Difficulty in breathing and shortness of breath
- Even simple activities of daily living can be hard due to breathing difficulties when the disease is progressed.
Complications
- Recurrent chest infections including Tuberculosis
- Lung cancer
- Increased pressure can occur in the lungs due to the formation of scar tissue
- Heart failure
- Arthritis
- Kidney disease
Diagnosis of Silicosis
The first step to diagnosing is through history by asking the patient about symptoms and exposure to silica dust in their work environment. A detailed work history can be used to understand the extent of your exposure to silica dust, including any possible measures that were implemented at your workplace to reduce dust inhalation.
Special Investigations
- Lung function (breathing) tests
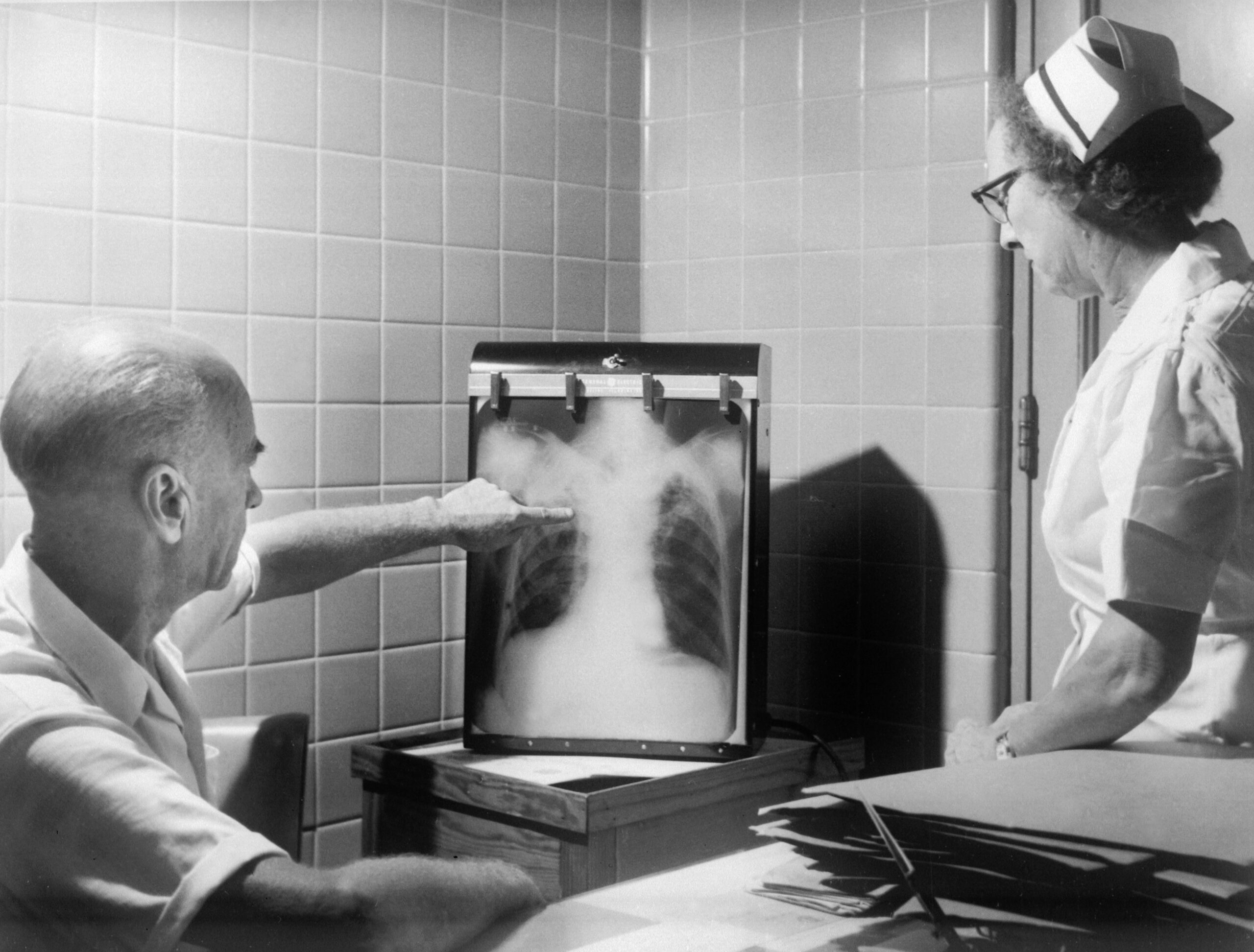
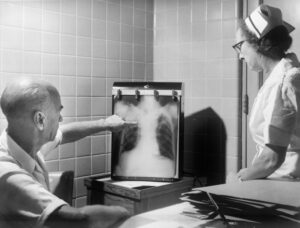
- Chest X-ray
- High-resolution CT scan (HRCT)
- Blood tests
- 6-minute walk test
- Bronchoscopy and biopsy are used
Management of Silicosis
As the scar tissue formation in the lungs caused by Silicosis is irreversible, treatment can not cure the disease completely. But symptoms can be managed while improving the quality of life in these patients using treatment methods.
Lifestyle Modification
- The most essential step is avoiding exposure to Silica dust and avoiding active or passive exposure to tobacco smoke as smoking can weaken your lungs more.
- It is important to get regular checkups to confirm whether you have got TB and you must get influenza and pneumococcal vaccines to the prevention of getting them
- Assessing mental health and providing proper psychological support is essential for these patients.
- Regular exercise can strengthen the lungs and reduce difficulty in breathing during daily activities.
- A healthy diet rich and balanced with all nutrients and adequate rest can also boost your health.

Pharmacological Management
- Drugs that dilate your airways can be given to minimize shortness of breath and ease the breathing of such patients.
- Oxygen therapy can also be given if required.
- If you get lung infections, antibiotic therapy can be given.
- Lung transplantation is the final option available.
Prevention of Silicosis
- If you are working in a high-risk industry for exposure to silica dust it is important to know about the risk of inhaling the dust and how it can affect your health.
- You must look for ways to protect your airway while working to minimize inhalation of silica dust.
- You must use the necessary equipment and adhere to proper methods to ensure your safety and protect your lungs from this dangerous dust.

References
- Kumar and Clerk’s Clinical Medicine -8th Edition- Parveen Kumar, Michael Clark
- Oxford Handbook of Clinical Medicine – 10th Edition