A fasting blood sugar test is also called a fasting blood glucose test, which is performed mainly to identify the glucose level in our body when we are fasting. Glucose is the type of sugar molecule that is utilized by our body to generate energy. Glucose is generated by breaking down the carbohydrates of the food you take. Maintenance of the glucose level in a healthy range is an essential mechanism to keep our bodies in good condition. This is mainly done by the hormone called insulin which is secreted by the pancreas.
Many issues can arise in the process of maintaining the glucose level of our body. Inadequate synthesis of insulin from the pancreas or due to defects in the insulin receptors of our body will affect mainly. These issues can give rise to abnormally high glucose levels that can lead to many complications. This condition with abnormally high glucose levels is called as diabetes mellitus.
A fasting blood sugar test is the main laboratory investigation used to diagnose diabetes mellitus. Fasting is the time in which the glucose level of our body should be at its lowest amount. First we need to measure the glucose concentration of our blood during fasting. Then we can understand whether our body’s glucose-lowering mechanisms are functioning adequately.
What are the Uses of this Test?
- Normally your medical officer will recommend you do this test as a first step. Then it will help to confirm you are having type 1 or type 2 diabetes mellitus and gestational diabetes mellitus. Diabetes mellitus is a very common disease among the modern population. Which gives rise to adverse complications such as heart diseases, chronic wounds, neurological defects, kidney diseases, and many more. This test can be performed as a part of your routine health check-up. And also if you are having clinical signs and symptoms suggestive of diabetes mellitus.
- Also, if you are having risk factors that make you predisposed to get diabetes mellitus such as obesity, family history of diabetes, sedentary lifestyle, and other comorbid conditions your doctor can recommend you get this test done.
- During pregnancy, the hormone changes that occur in your body make you predisposed to have high glucose levels in your blood. But abnormally high levels of glucose can give rise to a condition called gestational diabetes mellitus. This test can be performed to diagnose that condition as well.
- Also, if you have been previously diagnosed to be having diabetes mellitus and you are on antidiabetic drugs, then your medical officer will ask you to get this test done regularly. It will help to maintain the glucose levels in your body in a healthy range. As well as it can monitor your response to the treatment and reduce complications.
Clinical Features of Increased Blood Glucose Levels
If you are having following features, it is important to meet your medical officer and get yourself a fasting blood glucose test. Then it will help to identify whether you are having abnormally high glucose levels in your blood. Those features are as follows.
- Increased frequency of urination
- Increased feeling of thirst
- The recent loss of weight and loosening of clothes
- Tiredness and lightheadedness
- Getting recurrent infections such as urinary tract infections and respiratory tract infections
How to Prepare for the Fasting Blood Sugar Test?
This test requires some preparation, which includes fasting for 8 to 12 hours. You should avoid having food or drinks except for water for a minimum of 8 hours. But you will have to remain fasting for even 12 hours if you are undergoing some other investigations along with this test. Hence it is important to get advice about the exact time duration from your medical officer before the test.
If you are an already diagnosed diabetic patient, you will have to avoid taking your daily oral anti-diabetic drugs or insulin dose until the test is performed. As those drugs can lower your sugar levels and give false results. Normally this test is performed in the morning. After you have remained fasting overnight and your morning medications will be delayed until the test is over.
How Is the Procedure Done?
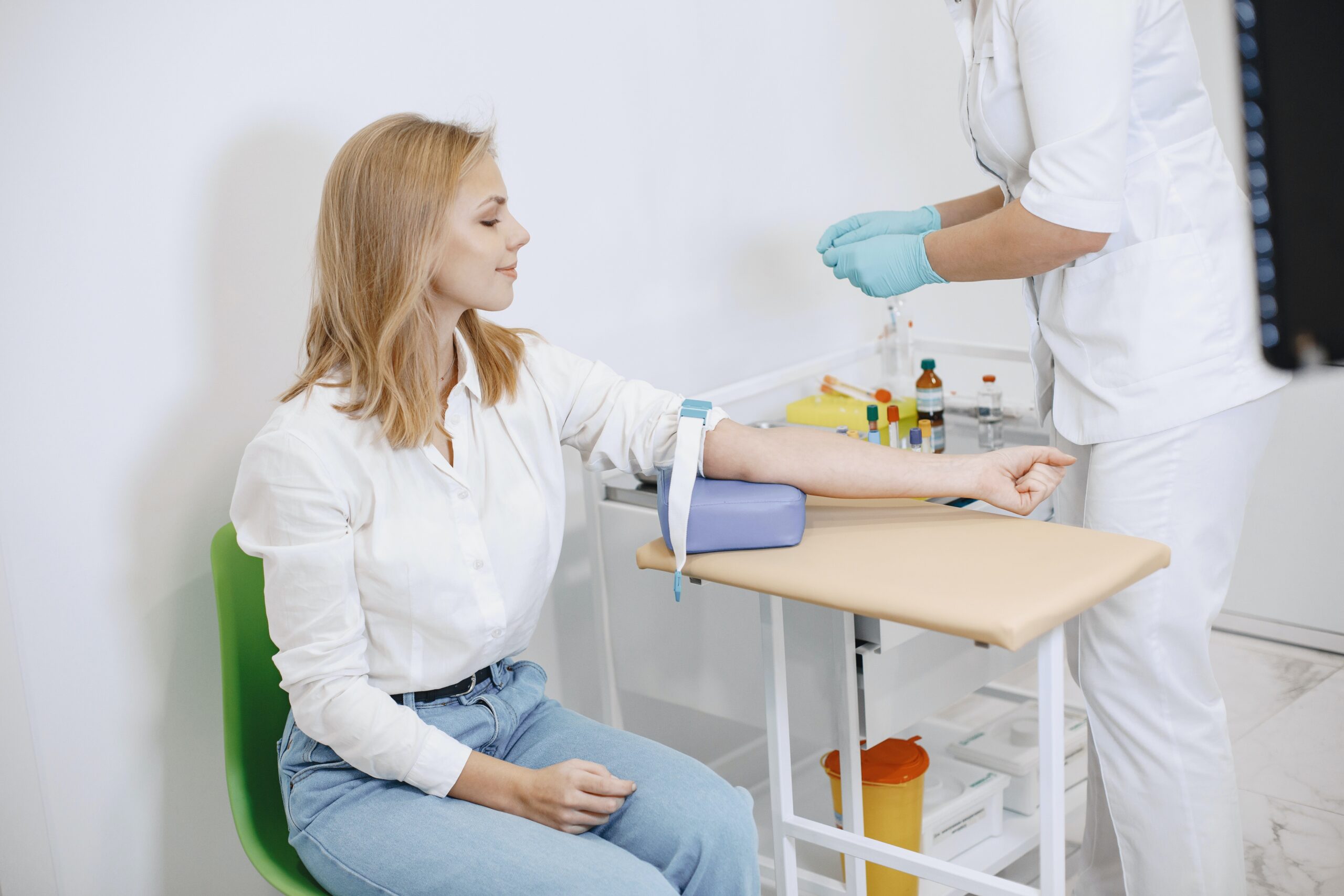
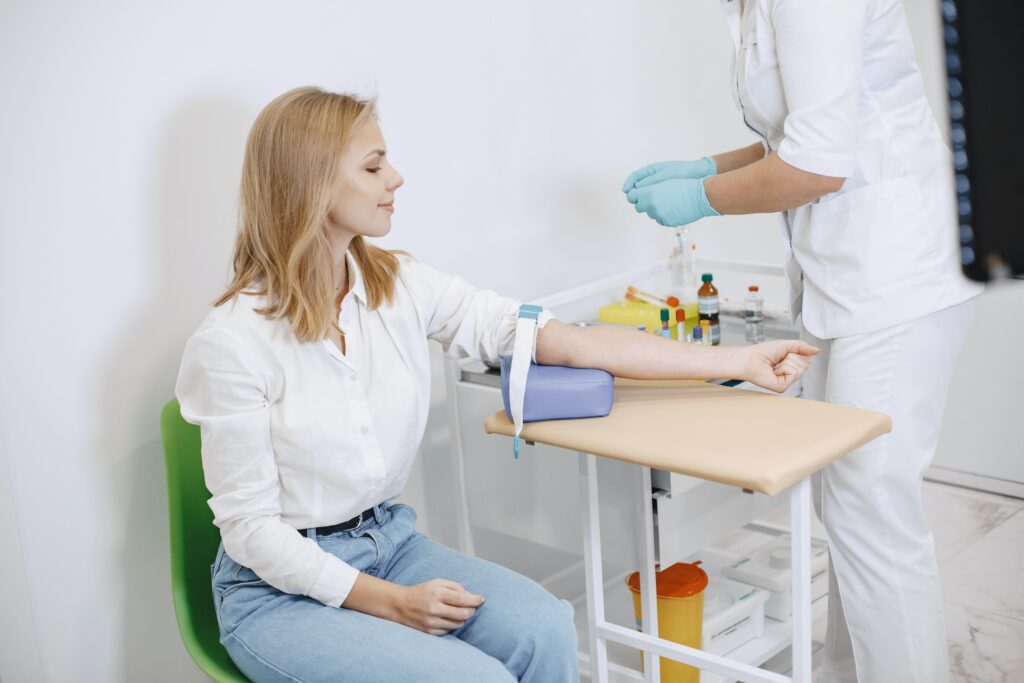
Normally the person who takes the blood sample will initially clean your arm and then insert a needle. Usually, blood is taken from the medial aspect of the middle of the arm and normally venous blood is taken for this test. The needle may sting or pinch a little initially, but it doesn’t hurt a lot. By inserting the needle, a sample of blood will be withdrawn and collected into a tube. Then the needle will be slowly removed while placing a bandage on your arm. The sample taken from you will be sent to the biochemistry laboratory for analysis.
After the test is done the pinched site will be covered by a piece of gauze on your arm. Also secured by a tape. You will feel sore around the site of injection for a few hours and later you may develop a small bruise at the injection site. You can return to your usual activities right after the test is performed. Also, the results of this test will be available for you within hours to days.
How to Interpret Results of the Fasting Blood Sugar Test?
- To have a normal blood sugar level in your blood the result must be between 3.9 to 5.4 mmols/l (70 to 99 mg/dl)
- If you are having a result between 5.5 to 6.9 mmol/l (100 to 125 mg/dl), you will be diagnosed with prediabetes or impaired glucose tolerance. If you are at this level, your medical officer will advise you to repeat your test in another 12 months to identify whether you are progressing toward getting diabetes. As this level is a bit above the normal range but not adequate to be diagnosed as diabetes mellitus and you are at a higher risk of getting the disease. But with adequate lifestyle modification steps, you can avoid getting the disease.
- If your result is 7.0 mmol/l (126 mg/dl) or above you will be diagnosed to be having diabetes mellitus.
What Can You Do if You Get High Fasting Blood Sugar Levels?
You need to meet your medical officer immediately to get advice regarding the management of your condition. If your doctor recommends you to have antidiabetic medications you must take them on time and have good compliance for medications.
Also, you need to follow certain lifestyle modification steps to avoid complications of diabetes as drugs alone will not be adequate to give a better result. You will have to engage in regular exercises, maintain your weight in a healthy range of BMI, have the recommended diet for diabetic patients, reduce sugar intake, avoid taking carbonated drinks, chocolates, and sweets as much as possible, and many more steps which will be further advised to you by your medical officer.
References
• Kumar and Clerk’s Clinical Medicine -8th Edition- Parveen Kumar, Michael Clark
• Oxford Handbook of Clinical Medicine – 10th Edition