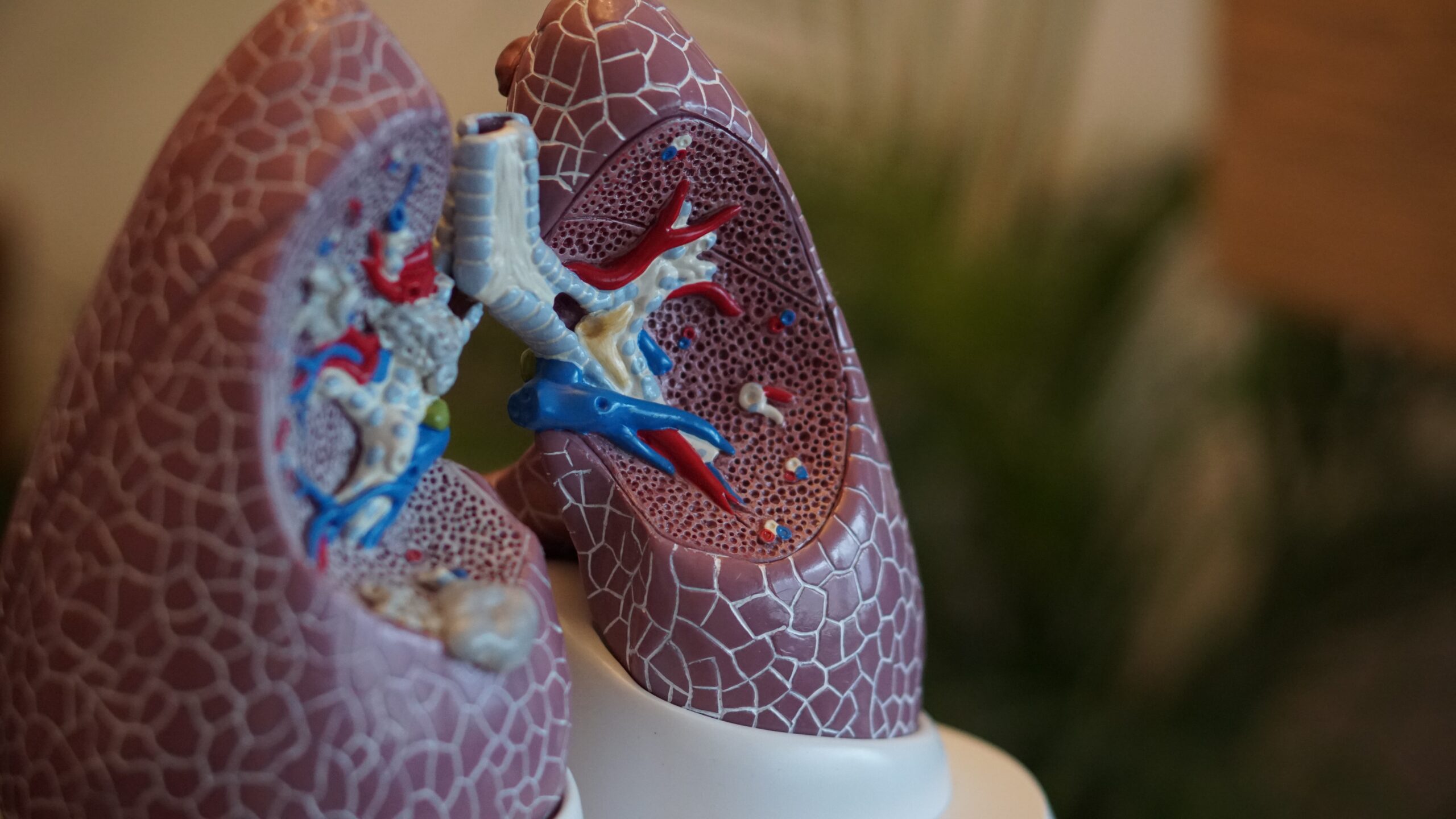
Cystic fibrosis is a disease that increases the viscosity and tenacity of mucous resulting in sticky mucous in the lungs and digestive system.
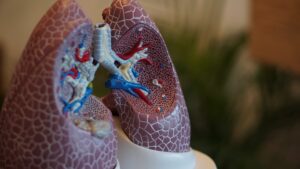
Increased production of sticky mucous attracts more infections in the lungs and digestive tract which becomes worse with time.
This disease can shorten life expectancy and no treatment was found to cure the disease completely.
Causes for Cystic Fibrosis
It is found to be caused due to inheritance of a faulty gene within the family. This familial predisposition along with recurrent respiratory tract infections can worsen the disease. This disease is not transmitted from person to person after birth. Hence only people with a positive family history of cystic fibrosis are at risk to get the condition.
Clinical Manifestations
Respiratory Tract
- Recurrent respiratory tract infections including pneumonia and cystic fibrosis are found to be the commonest reason to get recurrent chest infections in childhood.
- Abnormal growths called polyps can occur in the nose and sinusitis is very common in these patients.
- Breathing difficulties and blood-stained sputum noted during cough are also features in the later stages of the disease.

Gastrointestinal Tract
- A deficiency of the enzymes produced by the pancreas is observed which causes a lack of digestion of food and sticky smelly stools. These patients can also present with diarrhea and constipation.
- Increased occurrence of gallstones, gastrointestinal cancers, cirrhosis, and gastric ulcer disease is observed among these patients.
- Lots of patients find it difficult to put on weight and grow due to a lack of absorption and lack of digestion of food.
- Newborn babies can present with bowel obstruction due to large meconium which may need surgery.
- People with the condition can also develop a number of related conditions, including weakened bones due to osteoporosis, infertility in males, delayed puberty, and liver problems.
Diagnosis of Cystic Fibrosis
- Initial assessment of the patient using history and examination is important while looking for any positive family history.
- Analysis of salt concentration in sweat, DNA analysis in blood to detect any gene mutations, looking for radiological imaging tests to diagnose respiratory tract infections such as Bronchiectasis, and looking for structural defects in the male reproductive system are the main steps in the diagnosis of such patients.
Complications of Cystic Fibrosis
- Osteoporosis
- Diabetes
- Infertility
- Liver disease
- Nasal polyps and sinusitis
Management of Cystic Fibrosis
A complete cure is not found although many treatment modalities to reduce complications of the disease and improve the quality of life in such patients are being used currently.
Non-Pharmacological Management

- Patient education and proper nutrition are essential.
- Patients must be advised to stop smoking as it can affect the well-being of the lungs and worsen the effects of the disease.
- They must be given influenza and pneumococcal vaccinations.
- Methods to clear airways and remove sticky mucous in the lungs can improve breathing difficulties in these patients.
- Increased physical activities can also strengthen the functioning of the lungs.
- These patients need to have a diet rich in high calories and protein while taking vitamin and mineral supplements on a regular basis.
Pharmacological Management
- Antibiotic treatment is given for respiratory tract infections.
- Malnutrition and deficiency of pancreatic enzymes must also be treated accordingly.
References
- Kumar and Clerk’s Clinical Medicine -8th Edition- Parveen Kumar, Michael Clark
- Oxford Handbook of Clinical Medicine – 10th Edition